The European transport faces major challenges in terms of safety, greenhouse gas emissions, traffic congestion and its derived costs. In addition, the development of disruptive technologies and emergence of new mobility solutions generate a revolution in transport network and traffic management. In this context, TANGENT aims to develop new complementary tools for optimizing traffic operations in a coordinated and dynamic way from a multimodal perspective and considering automated/non-automated vehicles, passengers and freight transport. TANGENT will research on advanced techniques on modeling and simulation, optimization techniques for balancing the demand flows between the means of transport and users travel behavior modeling. As a result, a set of applications for decision-making support will be delivered creating a framework for coordinated traffic and transport management, encompassing an enhanced mobility information service and dashboard with associated APIs and advanced functionalities with a two-fold approach: to provide real-time traffic management recommendations and to support Transport Authorities to design network-wide optimal strategies. The framework also aims at supporting a multi-actor cooperation approach for transport network management by enabling communication channels. In this way, the services target to different actors in traffic management. The results will be tested in three case studies and the impact will be assessed to reach the expected reduction targets due to a more efficient management.
How We Contribute
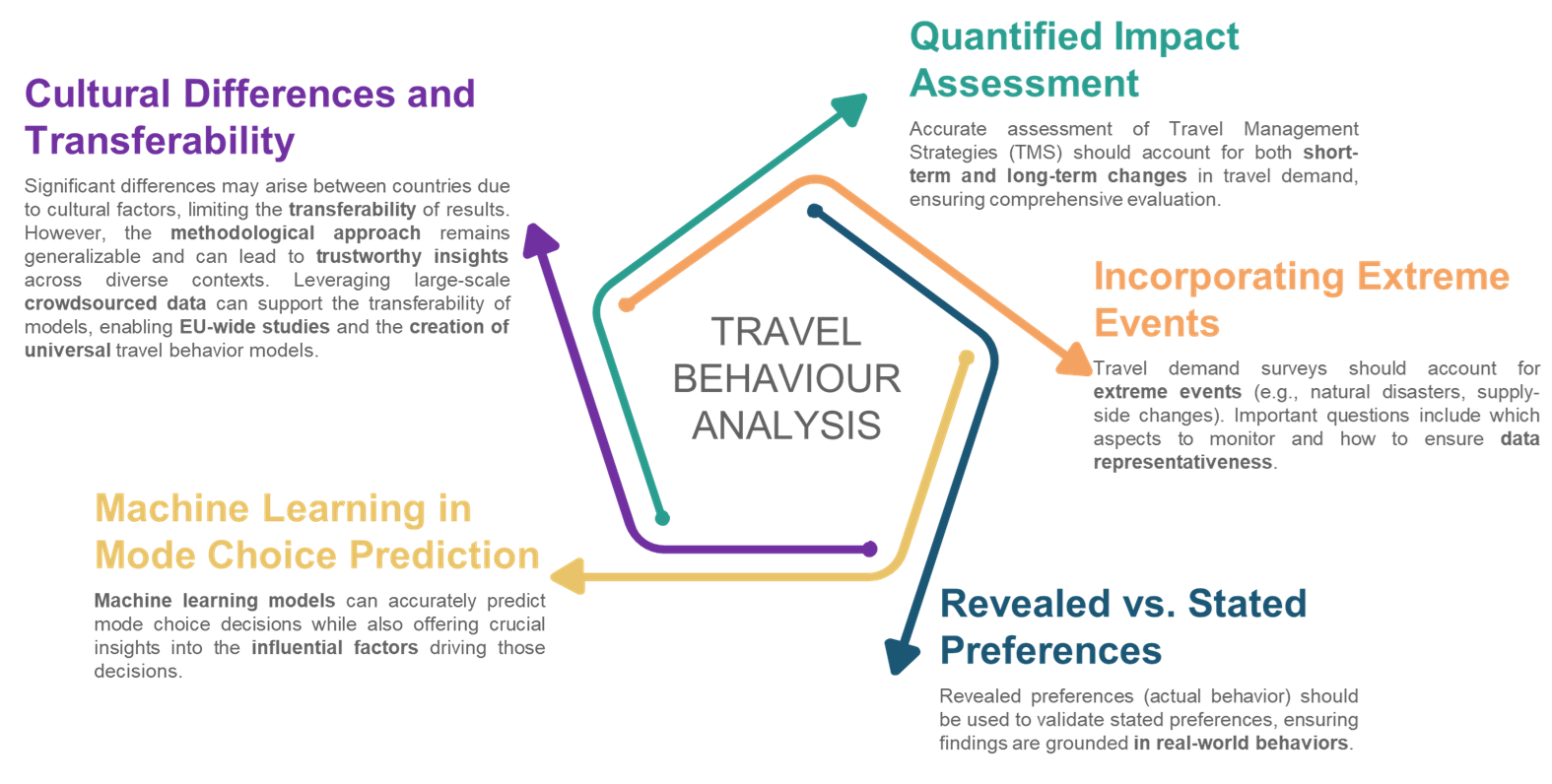
As a principal technical partner within TANGENT, DSAIT leads the development of a complete travel behavior module capable of quantitatively predicting urban travel mode selection for different commuter profiles and under various system conditions. Leveraging commuters’ actual behavior collected using state-of-the-art conversational surveys and actual mode choices inferred by shared trajectories, a complete set of econometric and machine learning models was developed and combined in a framework that leverages their complementariness in terms of interpretability and classification performance. The developed models allowed us to get a deep understanding of the socioeconomic and behavioral profiles of frequent users for each transportation mode, understand the circumstances that can cause switching modes during network disruptions and other extreme events and estimate ex-ante commuters’ reaction at the introduction of novel traffic management strategies, including dynamic congestion pricing and traffic control tools that prioritize public transit vehicles in signalized intersections.
DSAIT also introduced a novel, data-driven decision support mechanism designed to facilitate opinion consensus in environments with multiple stakeholders drawing on cutting edge quantitative frameworks such as Opinion Dynamics, Consensus Reaching Processes and various machine learning and optimisation techniques. The tool follows a modular design with specific submodules addressing the representation and elicitation of opinions, the identification of majority and minority opinions and spokespeople for each group and proposes algorithmic ways to handle opinion inconsistency and multitude. It can also provide guidance on identifying the key stakeholders that obstruct consensus and the issues where compromise is likely. The application and evaluation of the tool in a real decision-making setting in TANGENT’s case study cities demonstrated its capacity to facilitate the identification of an opinion that can be accepted by all participants in a cost- and time-effective manner.

